Earliest building blocks of the Milky Way discovered near its galactic heart
Mar 21, 2024, 4:22 PM
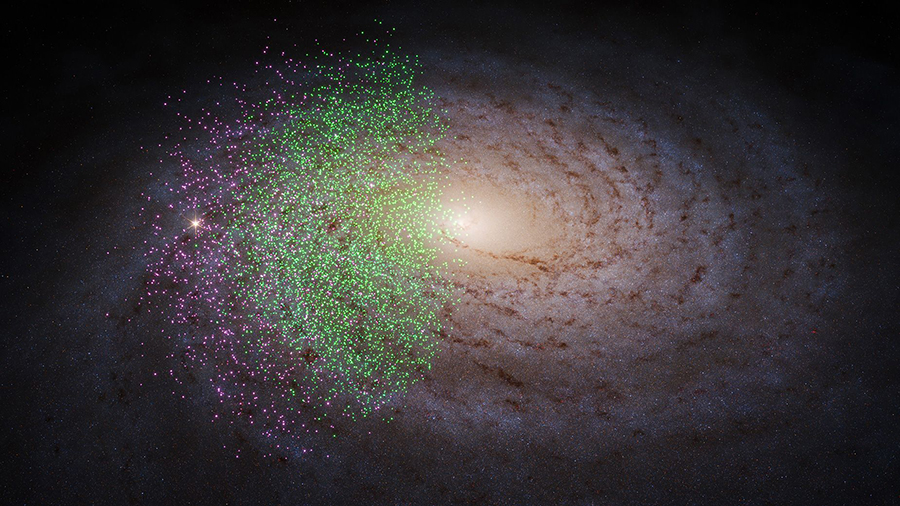
An illustration depicts the Milky Way galaxy from overhead, with green dots indicating Shiva stars and pink dots for Shakti stars. (S. Payne-Wardenaar/K. Malhan/MPIA via CNN Newsource)
(S. Payne-Wardenaar/K. Malhan/MPIA via CNN Newsource)
(CNN) — Astronomers have used the Gaia space telescope to spy some of the first building blocks of the Milky Way galaxy: two ancient streams of stars named Shakti and Shiva that helped our home galaxy grow and evolve more than 12 billion years ago.
Named after Hindu deities, the star streams appear to be the remnants of two galaxies that merged with an early version of the Milky Way between 12 billion and 13 billion years ago when the first galaxies were forming across the cosmos. The structures are so old that they formed well before the most ancient parts of the Milky Way’s iconic spiral arms and central disk.
A study detailing the observations appeared Thursday in The Astrophysical Journal.
“What’s truly amazing is that we can detect these ancient structures at all,” said lead study author Dr. Khyati Malhan, a postdoctoral scholar and Humboldt Research Fellow at Stockholm University in Sweden, in a statement. “The Milky Way has changed so significantly since these stars were born that we wouldn’t expect to recognise them so clearly as a group — but the unprecedented data we’re getting from Gaia made it possible.”

The distribution of Shakti (yellow) and Shiva (blue) stars can be seen near the heart of the Milky Way. (ESA/Gaia/DPAC/K. Malhan via CNN Newsource)
Observing Shakti and Shiva’s stellar wonders could help astronomers unlock the secrets of the Milky Way galaxy’s earliest days and the evolution of similarly massive galaxies throughout the cosmos, according to the researchers.
‘The first steps of our galaxy’s growth’
The Gaia space telescope, launched in 2013 by the European Space Agency, began observing the universe the following year. Astronomers have used Gaia’s observations to discover previously unknown structures in the Milky Way, helping them piece together the history of the galaxy. The telescope’s dataset has also provided astronomers with the positions, distances and movements for nearly 2 billion stars in the galaxy.
In 2022, study coauthor Hans-Walter Rix and his colleagues used Gaia to peer into the heart of the Milky Way and discovered the oldest stars ever found in the galaxy during their “galactic archaeology” observations. An analysis of data from nearly 6 million stars observed by Gaia and the Sloan Digital Sky Survey revealed two streams that appeared to stand out from the rest.
The survey data contained details about the chemical composition of the stars.
“We observed that, for a certain range of metal-poor stars, stars were crowded around two specific combinations of energy and angular momentum,” Malhan said.
Shakti and Shiva are near the Milky Way’s heart, and each stream is estimated to include the mass of about 10 million suns. Here, the ancient stars are all similar in age, orbital path and composition, which helped astronomers determine that both streams were likely threads from an outside source that wove together and became part of the Milky Way.
The researchers compared the discovery of Shiva and Shakti to finding the initial traces of an ancient settlement that eventually grew to become a large, modern city.
“The stars there are so ancient that they lack many of the heavier metal elements created later in the Universe’s lifetime. These heavy metals are those forged within stars and scattered through space when they die. The stars in our galaxy’s heart are metal-poor, so we dubbed this region the Milky Way’s ‘poor old heart,’” said Rix, director of the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy’s Department of Galaxies and Cosmology in Germany, in a statement.
“Until now, we had only recognised these very early fragments that came together to form the Milky Way’s ancient heart. With Shakti and Shiva, we now see the first pieces that seem comparably old but located further out. These signify the first steps of our galaxy’s growth towards its present size.”
Tracing galactic evolution
The Milky Way started out small and grew in size as it merged with other galaxies, gaining stars as well as hydrogen to form more stars. Each galaxy has hydrogen gas that aids in the birth of stars. As galaxies merge and collide, their hydrogen gas clouds are disrupted, which can create a frenzy of star birth.
Over time, the Milky Way’s long filaments of gas and dust coalesced and resulted in the modern spiral structure of the galaxy today.
Gaia has already helped astronomers to determine when the Milky Way experienced different merger events in the past, and future observations could unlock more insights.
“Revealing more about our galaxy’s infancy is one of Gaia’s goals, and it’s certainly achieving it,” said Timo Prusti, project scientist for Gaia at the European Space Agency, who was not involved in the study.
“We need to pinpoint the subtle yet crucial differences between stars in the Milky Way to understand how our galaxy formed and evolved. This requires incredibly precise data — and now, thanks to Gaia, we have that data. As we discover surprise parts of our galaxy like the Shiva and Shakti streams, we’re filling the gaps and painting a fuller picture of not only our current home, but our earliest cosmic history.”
The-CNN-Wire™ & © 2024 Cable News Network, Inc., a Warner Bros. Discovery Company. All rights reserved













