GENEVA (AP) — The World Health Organization said Friday that COVID-19 no longer qualifies as a global emergency, marking a symbolic end to the devastating coronavirus pandemic that triggered once-unthinkable lockdowns, upended economies and killed at least 7 million people worldwide.
WHO first declared COVID-19 to be an emergency more than three years ago. The U.N. health agency’s officials said that even though the emergency phase was over, the pandemic hasn’t come to an end, noting recent spikes in cases in Southeast Asia and the Middle East.
WHO says that thousands of people are dying from the virus every week, and millions of others report that they are still suffering from debilitating, long-term effects from the disease.
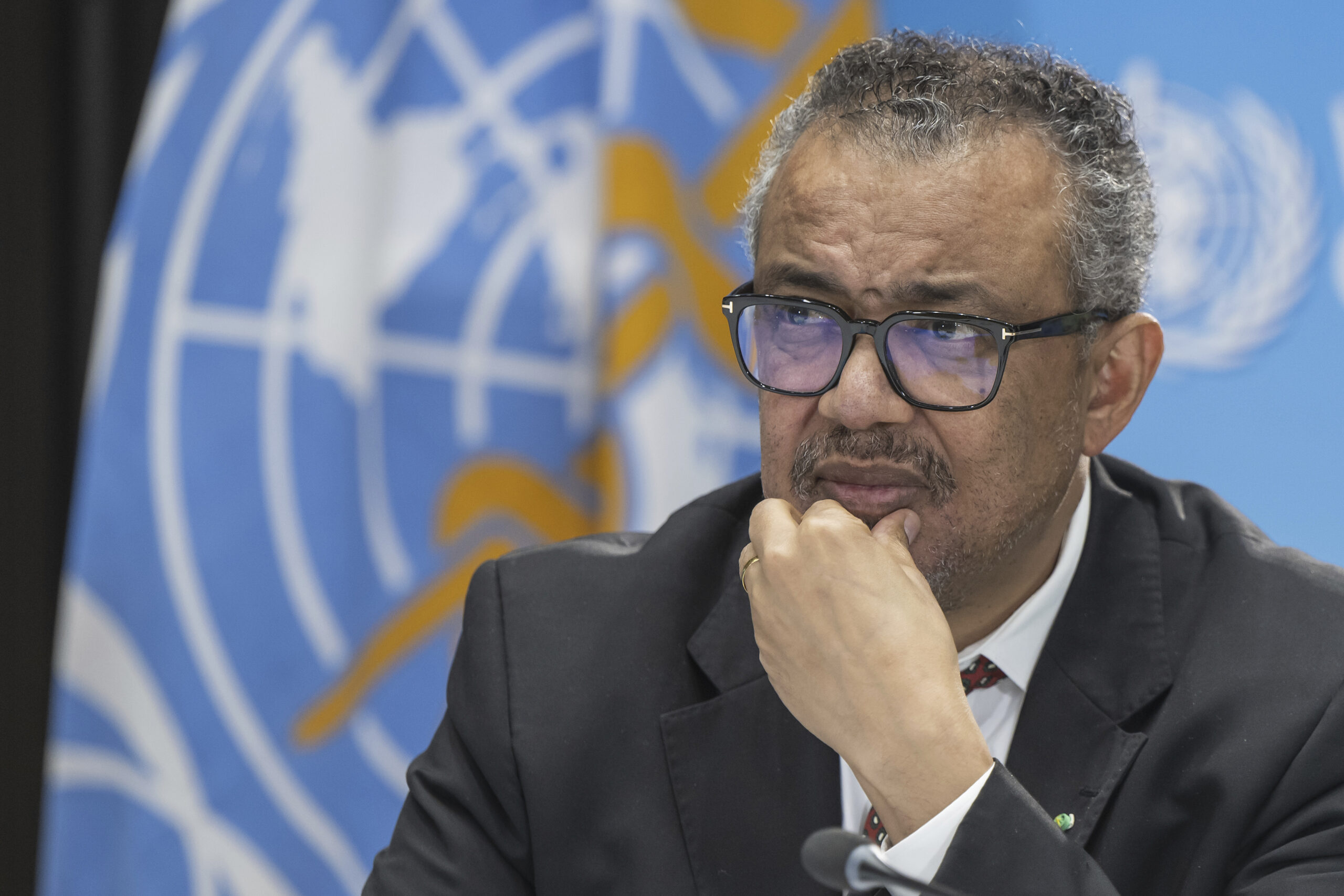
“It’s with great hope that I declare COVID-19 over as a global health emergency,” WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said.
“That does not mean COVID-19 is over as a global health threat,” he said, adding he wouldn’t hesitate to reconvene experts to reassess the situation should COVID-19 “put our world in peril.”
Tedros said the pandemic had been on a downward trend for more than a year, acknowledging that most countries have already returned to life before COVID-19.
He bemoaned the damage that COVID-19 had done to the global community, saying the pandemic had shattered businesses, exacerbated political divisions, led to the spread of misinformation and plunged millions into poverty. Tedros also noted that there were likely at least 20 million COVID-19 deaths, far more than the officially reported 7 million.
“COVID has changed our world and it has changed us,” he said, warning that the risk of new variants still remained.
Dr. Michael Ryan, WHO’s emergencies chief, said it was incumbent on heads of states and other leaders to decide on how future health threats should be faced, given the numerous problems that crippled the world’s response to COVID-19. Countries are negotiating a pandemic treaty that some hope may spell out how future disease threats will be faced — but it’s unlikely any such treaty would be legally binding.
When the U.N. health agency first declared the coronavirus to be an international crisis on Jan. 30, 2020, it hadn’t yet been named COVID-19 and there were no major outbreaks beyond China.
More than three years later, the virus has caused an estimated 764 million cases globally and about 5 billion people have received at least one dose of vaccine.
In the U.S., the public health emergency declaration made regarding COVID-19 is set to expire on May 11, when wide-ranging measures to support the pandemic response, including vaccine mandates, will end. Many other countries, including Germany, France and Britain, dropped many of their provisions against the pandemic last year.
When Tedros declared COVID-19 to be an emergency in 2020, he said his greatest fear was the virus’ potential to spread in countries with weak health systems.
In fact, some of the countries that suffered the worst COVID-19 death tolls were previously judged to be the best-prepared for a pandemic, including the U.S. and Britain. According to WHO data, the number of deaths reported in Africa account for just 3% of the global total.
WHO doesn’t “declare” pandemics, but first used the term to describe the outbreak in March 2020, when the virus had spread to every continent except Antarctica, long after many other scientists had said a pandemic was already underway.
WHO is the only agency mandated to coordinate the world’s response to acute health threats, but the organization faltered repeatedly as the coronavirus unfolded.
In January 2020, WHO publicly applauded China for its supposed speedy and transparent response, even though recordings of private meetings obtained by The Associated Press showed top officials were frustrated at the country’s lack of cooperation.
WHO also recommended against mask-wearing for the public for months, a mistake many health officials say cost lives.
Numerous scientists also slammed WHO’s reluctance to acknowledge that COVID-19 was frequently spread in the air and by people without symptoms, criticizing the agency’s lack of strong guidance to prevent such exposure.
Tedros was a vociferous critic of rich countries who hoarded the limited supplies of COVID-19 vaccines, warning that the world was on the brink of a “catastrophic moral failure” by failing to share shots with poor countries.
Most recently, WHO has been struggling to investigate the origins of the coronavirus, a challenging scientific endeavour that has also become politically fraught.
After a weeks-long visit to China, WHO released a report in 2021 concluding that COVID-19 most likely jumped into humans from animals, dismissing the possibility that it originated in a lab as “extremely unlikely.”
But the U.N. agency backtracked the following year, saying “key pieces of data” were still missing and that it was premature to rule out that COVID-19 might have ties to a lab.
Tedros lamented that the catastrophic toll of COVID-19 could have been avoided.
“We have the tools and the technologies to prepare for pandemics better, to detect them earlier, to respond to them faster,” Tedros said, without citing missteps by WHO specifically.
“A lack of (global) solidarity meant that those tools were not used as effectively as they could have been,” he said. “Lives were lost that should not have been. We must promise ourselves and our children and grandchildren that we will never make those mistakes again.”
___
Maria Cheng reported from London.